Hi, welcome to Gasgoo. In this episode of "Wheels of Change: Stories of Chinese Auto Giants," let's talk about Xiaomi.
Technical foundation
Before the Xiaomi SU7 was launched, the market had doubts about Xiaomi's foray into car manufacturing. One major concern was the actual value of Xiaomi EV's technologies. After all, building core technology development capabilities in a short time is no easy task. There was a lot of speculation that Xiaomi was relying heavily on suppliers.
However, the successful Xiaomi EV technology launch event last year and the volume production and rollout of the Xiaomi SU7 this year have effectively addressed these doubts.
Xiaomi EV's five core technologies—E-motor, Battery, Xiaomi Hyper Die-Casting, Xiaomi Pilot Autonomous Driving, and Smart Cabin—form the foundation of Xiaomi's competitive edge in electrification and intelligence.
In terms of electrification, Xiaomi EV advances its technology through both independent R&D and joint development.
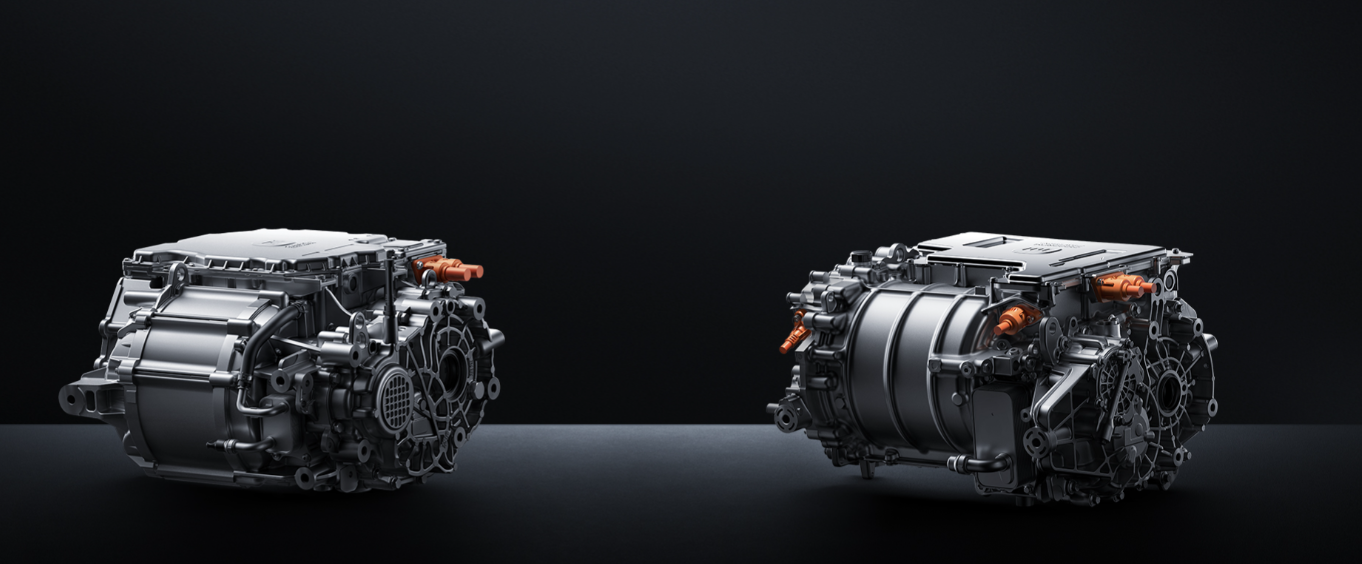
Left: HyperEngine V6; right: HyperEngine V6s; photo credit: Xiaomi EV
Specifically, Xiaomi EV's electric drive system, particularly its E-motor technology, is one of its core advantages. Currently, Xiaomi EV features three HyperEngines: V6, V6s, and V8s. The HyperEngine V6 and V6s, boasting a rotational speed of 21,000 rpm, are co-developed with UAES (United Automotive Electronic Systems) and INOVANCE Automotive.

HyperEngine V8s; photo credit: Xiaomi EV
Xiaomi independently developed and produced its third E-motor, the HyperEngine V8s, which reaches a speed of 27,200 rpm. To develop the V8s, Xiaomi improved materials, redesigned the motor cooling system, and equipped it with Xiaomi's self-developed SiC electric control module. The entire development process involved applying for 155 patents, with 60 patents already granted. The recently unveiled Xiaomi SU7 Ultra Prototype is equipped with the HyperEngine V8s.
Additionally, Xiaomi EV's next-generation hyper E-motor, using carbon fiber laser curing winding technology, has achieved a maximum rotor speed of 35,000 rpm in the lab.
In terms of batteries, Xiaomi self-developed an 800V SiC high-voltage platform, with a maximum voltage of 871 volts. Furthermore, Xiaomi EV collaborated with CATL, investing thousands of engineers and spending more than two years in co-developing the Xiaomi 800V high-voltage battery pack.
Notably, Xiaomi EV's Inverted Cell Technology inverts the battery cells and pressure relief valves, further freeing up cabin space. By the end of 2023, Xiaomi EV had applied for 132 patents in the battery field, with 65 patents granted.
Since entering the smartphone market in 2010, Xiaomi has accumulated comprehensive technical capabilities in operating system, AI, robotics, and more. These capabilities will gradually be applied to its automobiles.
In terms of intelligent driving, Xiaomi EV unveiled its self-developed full-stack intelligent driving technology framework last year, pioneering three key technologies: Adaptive BEV Technology, Road-Mapping Foundational Model, and Super-Res Occupancy Network Technology. . The Super-Res Occupancy Network was accepted by the top international computer vision conference CVPR in early 2024.
Xiaomi claims to be the first in China to achieve mass production of end-to-end large model technology in intelligent driving. This model replaces multiple modules previously used for perception, decision-making, and planning, allowing intelligent driving system to directly input images at one end and output driving trajectories at the other. Using this algorithm, Xiaomi EV has achieved a minimum granularity of 5cm in extremely narrow parking spaces and a maximum valet parking cruising speed of 23 km/h.

Xiaomi develops its own intelligent driving system Xiaomi Pilot; photo credit: Xiaomi
Currently, Xiaomi's intelligent driving system is available in two solutions: the Xiaomi Pilot Pro and the Xiaomi Pilot Max. Both of them ride on the NVIDIA DRIVE Orin computing platform and feature 11 cameras, all utilizing the Adaptive BEV Technology and end-to-end large model.
The main difference between them is that the Max version includes two additional rear-facing corner millimeter-wave radars and one LiDAR unit. It also has an extra Orin chip compared to the Pro version, providing a computing power of up to 508 TOPS.
Xiaomi EV aims to enter the top tier by 2024 regarding intelligent driving, and to achieve this goal, Xiaomi has provided substantial financial support. Mr. Lu Weibing revealed that Xiaomi is firmly committed to investing in intelligent driving, with an initial investment of about 4.7 billion RMB and a budget of about 1.5 billion yuan for this year, with a tendency to ramp up. At present, Xiaomi's dedicated intelligent driving team has exceeded 1,000 members, and at the beginning of 2024, it established an autonomous driving R&D center in Wuhan, with plans to expand the team by another 500 people by the end of the year.
Now, the Xiaomi SU7's all variants support highway NOA (Navigate on Autopilot) and valet parking functions nationwide. On May 31, Xiaomi EV announced that it would gradually roll out the urban NOA function in ten cities across the country to advanced intelligent driving version’s users who have achieved a safe driving distance of 1,000 km. By the end of August, Xiaomi aims to enable urban NOA countrywide.
As for the smart cabin, the Xiaomi SU7 comes standard with the Snapdragon 8295 in-car chip across its entire lineup. Based on the Xiaomi HyperOS, Xiaomi has built a unified visual interaction system, achieving a fully shared ecosystem from software to hardware. Compared to other in-car systems, the Xiaomi HyperOS is also commendable.
From the outset, the Xiaomi Smart Cabin was designed to integrate phones and tablets as part of the cockpit, implementing a multi-end unified native design for cross-device control. Notably, to meet the needs of users, Xiaomi EV fully supports CarPlay, the mounting of iPads and iPad accessories, and applications on the rear extension mount.
Xiaomi has also introduced the CarIoT ecosystem, which is fully open to third parties, featuring standardized interfaces, extensive communication protocol standards, and lightweight retrofit solutions for existing devices. For instance, the four sides of the central control screen support hardware ecosystem expansion, allowing traditional physical dials to be installed on the central control screen through magnetic suction.
Moreover, Xiaomi's self-developed sound large model made its debut on July 19. It can recognize various natural and everyday sounds, such as a baby crying or water droplets, and understand the environment and emotions behind the sounds. This model will first be applied to the Xiaomi SU7, introducing an external wake-up defense function, and is set to be available across all trims by August 2024.
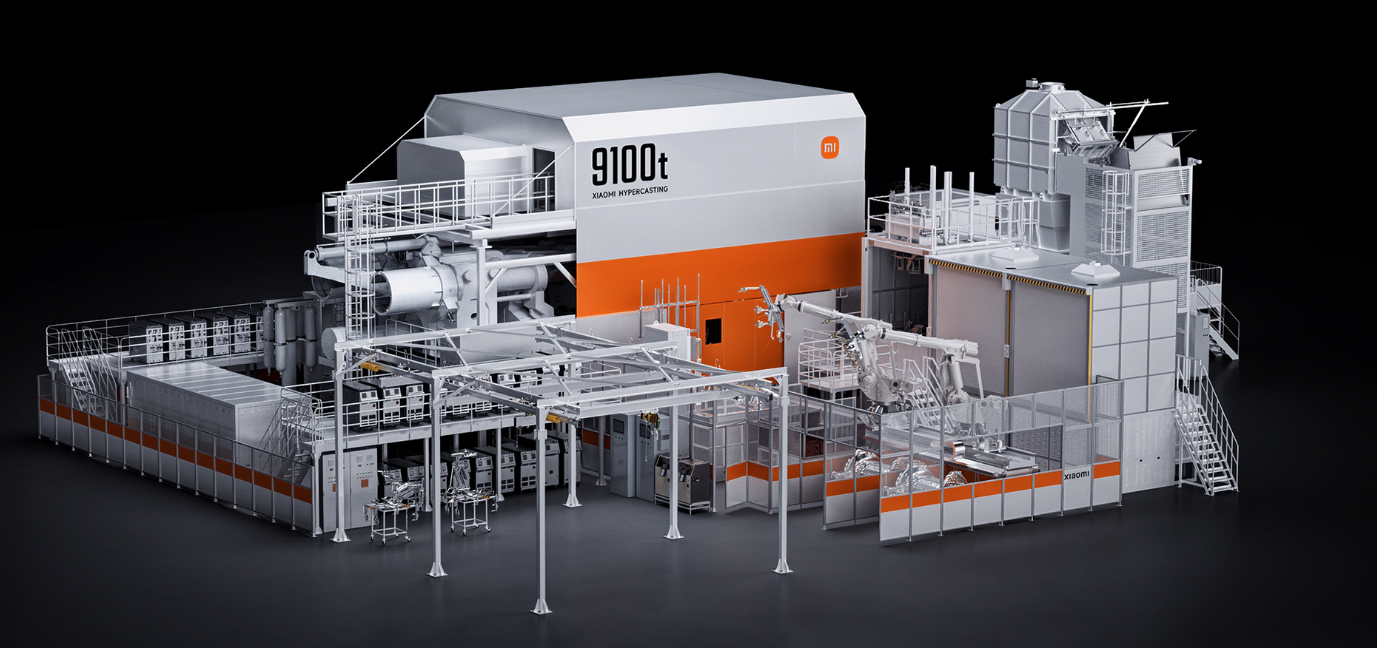

Xiaomi HyperCasting; photo credit: Xiaomi EV
Xiaomi EV's fifth core technology is its self-developed Hyper Die-Casting T9100 cluster. In practical use, the maximum clamping force of the Xiaomi Hyper Die-Casting is 9,500t, stabilizing at 9,300t.
Clamping force is not the only metric for large die-casting technology. The performance of heat treatment-free alloy materials, die-casting island cluster design, and defect detection are also core indicators of large die-casting technology.
In material R&D, Xiaomi has developed Xiaomi Titans Metal, a high-strength, high-resilience, heat-treated die-casting material.
For now, Xiaomi is one of only two companies worldwide, and the only one in China, with self-developed heat treatment-free alloy materials and self-developed large die-casting island cluster.
The 9100t die-casting machine, co-developed by Xiaomi and Haitian Die Casting, incorporates 11 patented design innovations, most of which are invention patents. However, the die-casting machine is just one part of the whole process; Xiaomi said it has self-developed the entire die-casting cluster system, which includes 60 devices and 433 process parameters.The application of large die-casting technology in the automotive industry has indeed become a development trend. Tesla is one of the strong adopters. It is expected that in the coming years, as die-casting machine tonnage continues to grow and mold technology improves, the large die-casting technology will see wider application in the car manufacturing industry.
Xiaomi EV's technology development goals are essentially included within the Xiaomi EV Modena technology framework.
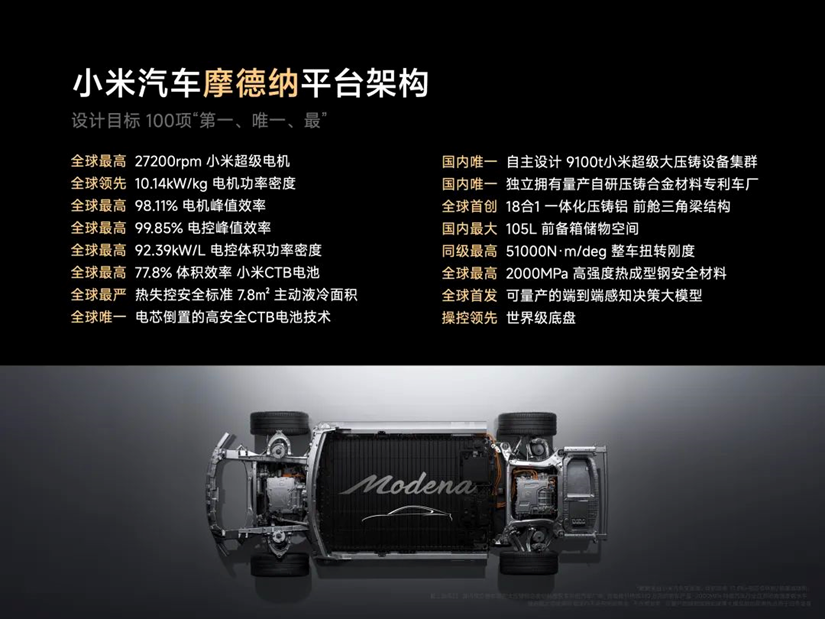
Modena technology framework; photo credit: Xiaomi EV
According to the Gasgoo Auto Research Institute, the Modena technology framework represents a significant leap for Xiaomi's Human x Car x Home ecosystem, integrating intelligent driving, smart cabin, electric power systems, vehicle networking, and big data. This framework achieves a comprehensive upgrade of vehicle technologies, providing users with an intelligent, safe, and efficient travel experience.
Realizing these technologies is not easy, mainly thanks to Xiaomi's willingness to invest huge human and capital resources in R&D. As of March 31, 2024, Xiaomi's R&D personnel numbered 17,421, accounting for 49.2% of the total workforce.
Xiaomi's R&D investment has been steadily climbing over the years. In 2023, its total R&D expenditure reached 19.1 billion RMB, a year-on-year increase of 19.2%. In the first quarter of this year, its R&D spending reached 5.2 billion RMB, up 25.4% year on year. Additionally, expenses for Xiaomi's innovative businesses, including smart cars, grew to 6.7 billion RMB last year and have already reached 2.3 billion RMB in the first quarter of this year.
Lei Jun pointed out that 14 years ago, when Xiaomi was established, it chose a "light business model," which led to rapid initial growth but lacked a solid foundation. This resulted in many setbacks over time, and Xiaomi is still making up for it until now. So, when Xiaomi started its new ventures, it decided not to take shortcuts, avoiding acquisitions and outsourcing. Instead, it focused on in-house R&D of core technologies, committing to investing ten times more.
Xiaomi's investments have borne fruit. Now, with the participation of Xiaomi EV, Xiaomi's Human x Car x Home ecosystem has come full circle. Intelligent driving, smart cabin, and the ecosystem will be Xiaomi EV's technological edge in the competition.
Importance of building ecosystem
In the era of smart electric vehicles, the focus is no longer solely on individual car products or technologies; the ability to build and operate an entire ecosystem has become the key factor to success.
Xiaomi EV's ecosystem can be understood on two levels: one is Xiaomi's Human x Car x Home ecosystem, and the other is its layout in industrial chain.

Photo credit: Xiaomi EV
Starting with the Human x Car x Home ecosystem, at the end of October 2023, Xiaomi announced a comprehensive upgrade of its corporate strategy, shifting from the "Smartphone x AIoT" to the "Human x Car x Home" ecosystem, which is a unique advantage for Xiaomi EV. Backed by Xiaomi, the world's third-largest smartphone manufacturer and the largest consumer IoT platform, Xiaomi EV leverages the HyperOS to achieve seamless connection and real-time coordination across human, cars, and homes.
Specifically, for "Human," Xiaomi focuses on smartphones and smart wearable devices, providing users with personalized and convenient smart life services.
For "Car," Xiaomi uses smart technologies to create an intelligent in-car ecosystem, turning the car into a mobile living space and smart terminal.
For "Home," Xiaomi's smart home products cover all aspects of life, forming a complete suite of smart home solutions.
Xiaomi has set the Human x Car x Home ecosystem as its overall development strategy, which can be broken down into six sub-strategies, namely, high-end strategy, industry-leading capability strategy, OS strategy, AI strategy, chip strategy, and new retail strategy.
Xiaomi's Human x Car x Home ecosystem strategy is already showing its power. In the first quarter of 2024, Xiaomi achieved total revenue of around 75.5 billion RMB, a year-on-year jump of 27%. The adjusted net profit was 6.5 billion RMB, zooming up 100.8% year on year.
Regarding business segments, in the first quarter, Xiaomi's global smartphone shipments reached 40.6 million units, a year-on-year leap of 33.7%. As of March 31, 2024, the number of IoT devices connected to Xiaomi's AIoT platform increased by 27.2% year-on-year to 786 million units.
Although Xiaomi EV's contribution was very little in the first quarter, the implementation of the Human x Car x Home ecosystem strategy has undoubtedly broadened Xiaomi's potential, showing more possibilities to the market.
In this year's first-quarter earnings call, Lu Weibing stated that with the hot sales of the Xiaomi SU7, the high-end breakthroughs in both smartphones and cars are expected to drive other categories going upscale. Overall, the Human x Car x Home ecosystem will be key to maintaining Xiaomi's competitiveness, with Xiaomi EV at its core.
The second ecosystem is Xiaomi EV's industrial ecosystem. As a seasoned player in the supply chain, Xiaomi has chosen to enter the automotive industry by leveraging its expertise in supply chain layout.
According to official disclosures and information collected by Gasgoo Auto Research Institute, the suppliers for the Xiaomi SU7 include giants like CATL and Bosch, some of which are companies where Xiaomi serves as a shareholder. Investment in the supply chain is a core part of Xiaomi's industrial ecosystem.
It is roughly estimated that Xiaomi, through investment institutions such as ShunWei Capital, Xiaomi Industrial Investment Fund, and Xiaomi Intelligent Manufacturing Equity Investment Fund, has invested in nearly 100 automotive supply chain companies. These investments cover various fields, including automotive-grade chips, LiDAR, intelligent driving software solutions, drive-by-wire actuators, power batteries, and battery raw materials. Companies like Zhejiang EVTECH Co., Ltd. and Hesai Technology are among the suppliers where Xiaomi holds equity stakes.
Xiaomi's investment efforts still continue. According to Tianyancha, Beijing Contemporary Amperex Power Battery Co., Ltd. was incorporated on May 17 this year, and it will build an intelligent battery cell manufacturing plant in Beijing. This company is 51% owned by CATL, 39% by BAIC Lanhaixin (a subsidiary of BAIC Group), and 5% each by Beijing Energy Holding Co., Ltd. and Xiaomi EV.
This comprehensive investment strategy covers almost all aspects of the automotive industry, ensuring the consistency, stability, and efficiency of Xiaomi EV's supply chain. It also enhances Xiaomi's decision-making influence within the automotive supply chain.
Overall, Xiaomi EV has demonstrated its technical strength, industrial layout, and market potential in its carmaking venture. However, the road ahead is still fraught with challenges. Fierce market competition, rapid technology iteration, and rising consumer expectations all pose higher demands on Xiaomi EV.
As Lei Jun remarked, "Building cars is tough, but success will be very cool." The future path of Xiaomi EV holds many uncertainties, but these challenges will drive the company's progress.
Xiaomi EV is ambitious to become one of the world's top five carmakers by 2030. We look forward to Xiaomi EV achieving its success.
联系邮箱:info@gasgoo.com
求职应聘:021-39197800-8035
简历投递:zhaopin@gasgoo.com
客服微信:gasgoo12 (豆豆)

新闻热线:021-39586122
商务合作:021-39586681
市场合作:021-39197800-8032
研究院项目咨询:021-39197921
